Introduction:
The Ideal URL Structure is the most important in search engine optimization (SEO); every aspect of your website determines its visibility and ranking on search engines. One often overlooked yet vital element is the URL structure. A well-designed URL structure improves user experience and enhances your website’s SEO performance. In this article, we will compare hierarchical and flat URL structures, highlighting their benefits, drawbacks, and best practices for optimizing them.
Choosing the right URL structure is crucial for SEO successUnderstanding URL Structures
Before we dip into the comparison, it is essential to understand what URL structures are and how they affect your website. A URL (Uniform Resource Locator) is a web address that provides a unique identifier for each page on your site. It consists of several components: the protocol (e.g., https://), domain name, subdomain, directory, and the page’s filename. The structure and organization of these components determine the URL structure.
The Importance of Ideal URL Structure for SEO
URL structure plays a significant role in SEO for several reasons. First and foremost, search engines use URLs to understand the content and hierarchy of your website. A clear and logical URL structure makes it more comfortable for search engine bots to crawl and index your pages, ultimately leading to better visibility in search results.
Additionally, a well-optimized URL structure can improve the user experience. A concise and descriptive URL gives users a conception of what to expect when clicking on a link, increasing the likelihood of click-throughs and reducing bounce rates.
Hierarchical URL Structure
A hierarchical URL structure arranges pages in a tree-like structure, reflecting the site’s organization and content hierarchy. It typically includes subdirectories to categorize content and improve user navigation.
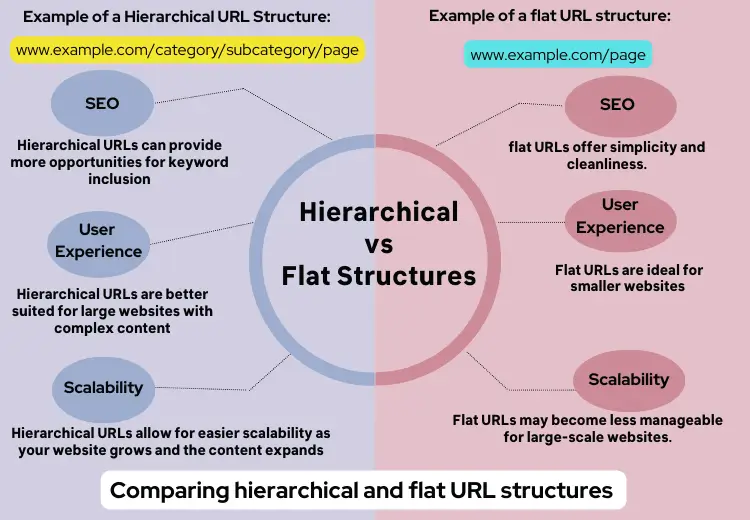
Example of a Hierarchical URL Structure:
www.example.com/category/subcategory/page
Here, each level of the hierarchy is separated by forward slashes (/), indicating the relationship between pages.
Advantages of Hierarchical URL Structure
- Organizational Structure: Hierarchical URLs provide a logical and organized representation of your website’s content hierarchy, making it more comfortable for users and search engines to understand the site structure.
- Keyword Placement: By incorporating relevant keywords in the directory structure, hierarchical URLs can signal to search engines the topic or theme of the page, enhancing keyword optimization.
- User-Friendly Navigation: A well-structured hierarchy can enable users to navigate your website more intuitively, leading to a better user experience.
Disadvantages of Hierarchical URL Structure
- Lengthy URLs: A hierarchical structure can sometimes result in long and complex URLs, which can be less user-friendly and difficult to share or link to.
- Restrictive Structure: Implementing changes to the structure, such as reorganizing categories or moving pages, can be challenging and may require redirects to maintain SEO equity.
Best Practices for Hierarchical URL Structure
- Maintain a shallow structure: Limit the number of subdirectories to avoid excessively long URLs and improve user experience.
- Use descriptive keywords: Include relevant keywords in the names of the directory to improve search engine visibility and user understanding.
- Maintain consistency: Ensure consistency in naming conventions and structure throughout the site to provide a seamless user experience.
Flat URL Structure
A flat URL structure aims to keep URLs concise and devoid of unnecessary subdirectories. It is often used for smaller websites with fewer categories or pages.
Here is an example of a flat URL structure that typically includes all pages at the same level, like so:
www.technicalsp.com/page
Advantages of Flat URL Structure
- Simplicity and Readability: Flat URLs are typically shorter, cleaner, and easier to read, making them more user-friendly and shareable.
- Easy Maintenance: With fewer directories, a flat structure allows for easier reorganization and page movement without requiring extensive redirects.
- Topical Relevance: Flat URLs can focus on the main topic or keyword by eliminating unnecessary subdirectories, potentially boosting search engine visibility.
Disadvantages of Flat URL Structure
- Limited Categorization: The absence of subdirectories can make categorizing and organizing content challenging, potentially confusing users and search engines.
- Less Keyword Placement: With hierarchical directories, the opportunity to signal keywords to search engines may be expanded, potentially impacting SEO performance.
Best Practices for Flat URL Structure
- Use descriptive filenames: Incorporate relevant keywords directly into the page filename to enhance keyword optimization.
- Utilize breadcrumbs: Implement breadcrumb navigation to provide context and aid users in understanding the site’s structure.
- Leverage metadata: Compensate the lack of directory structure by using meta tags and other on-page optimization techniques to signal topical relevance.
Comparing Hierarchical and Flat URL Structures
Both hierarchical and flat URL structures have their advantages and considerations. Here’s a brief comparison to help you make a knowledgeable decision:
- SEO: Hierarchical URLs can provide more opportunities for keyword inclusion, while flat URLs offer simplicity and cleanliness.
- User Experience: Hierarchical URLs are better suited for large websites with complex content, providing organization and structure. Flat URLs are ideal for smaller websites or those with straightforward content, enhancing user-friendliness.
- Scalability: Hierarchical URLs allow for easier scalability as your website grows and the content expands. Flat URLs may become less manageable for large-scale websites.
Choosing the Ideal URL Structure
Deciding between a hierarchical or flat URL structure depends on different elements, such as the size and complexity of your website, your content organization, and the overall user experience you want to provide. A hierarchical structure works best for larger websites with diverse content and clear categorization. On the other hand, a flat structure suits smaller websites or those with a more straightforward content structure.
URL Structure and Keyword Optimization
Regardless of the chosen structure, keyword optimization is crucial for SEO. Incorporate relevant keywords in your URLs, but keep them concise and readable. Steer clear of excessive keyword usage, as it can adversely affect user experience and search engine rankings.
User-Friendly URLs
Use descriptive words to create user-friendly URLs and avoid unnecessary parameters or special characters. Make them intuitive and easy to remember. Remember that user experience should always be a top priority.
URL Structure and Site Navigation
Your URL structure should align with your website’s navigation to provide a seamless user experience. Ensure that users can easily navigate between different sections or categories by following the URL structure.
URL Structure and Mobile Optimization
With the increasing use of mobile devices, optimizing your URL structure for mobile is essential. Ensure your URLs are responsive and mobile-friendly, allowing users to access and navigate your site seamlessly across various devices.
Measuring and Monitoring URL Structure Performance
Regularly monitor the performance of your URL structure using web analytics tools. Track metrics such as organic traffic, bounce rates, and time on the page to assess the effectiveness of your chosen structure. Make adjustments as needed to improve SEO and user experience.
Conclusion
Choosing the ideal URL structure for your website is critical to optimizing your SEO performance. Whether you opt for a hierarchical or flat structure, it’s crucial to prioritize user experience, keyword optimization, and adherence to best practices. Regularly monitor your URL structure’s performance and adjust as needed to ensure it remains SEO-friendly and user-friendly. By considering your website’s unique needs and implementing an effective URL structure, you can improve your website’s visibility, search engine rankings, and overall success online.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ):
Q: Which URL structure is better for SEO?
Hierarchical and flat URL structures can be effective for SEO if implemented correctly. The best structure for your website depends on factors such as the size and sophistication of your site, content organization, and user experience goals. It’s essential to consider your specific requirements and choose a structure that aligns with your overall SEO strategy.
Q: Can I change my URL structure without affecting SEO?
Changing your URL structure can impact your SEO, especially if not done correctly. When making changes, it’s crucial to set up appropriate redirects from old URLs to new ones to ensure that search engines can always find and index your pages. Additionally, updating internal links and notifying search engines of the changes through sitemaps can help mitigate any potential negative effects on SEO.
Q: How long should my URLs be?
Ideally, URLs should be concise and descriptive. Long URLs can be challenging for users to remember and share, and they may also get truncated in search engine results. Aim for short URLs focused on the main topic or keyword, and provide a clear indication of the page’s content.
Q: What is the role of keywords in URL structures?
Keywords in URL structures can signal to search engines the topic or theme of a page. Including relevant keywords in your URLs can improve your website’s visibility and ranking for those keywords. However, using keywords naturally and avoiding keyword stuffing is important, as this can harm both SEO and user experience.
Q: . Is it necessary to include keywords in every URL?
While including keywords in URLs can benefit SEO, having them in some URLs is okay. Focus on incorporating keywords in URLs where they make sense and accurately reflect the page’s content. Remember that user experience and readability are equally important, so prioritize creating concise, descriptive, and user-friendly URLs.



